ARTHRITIS WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW MORE ABOUT?
Lifestyle
changes have welcomed various health concerns like overweight, reduced bone
density, infertility, etc.; which are indeed responsible for variety of
underlying dangerous conditions such as arthritis. It has been estimated that
around 50% people, over the age 65 can have arthritis. Hence, indeveloped
countries, arthritis can be one of the leading health issues, which need to be
tackled well within time to avoid increased social economic burden.
Arthritis can be categorized as an inflammatory, joint disorder; affecting
multiple joints at a time. The condition has more than 100 subdivisions, with
osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis as the most common forms. It is simply known
to be a slowly progressive disease, affecting persons of any age groups;
although women are known to be more prevalent than men.
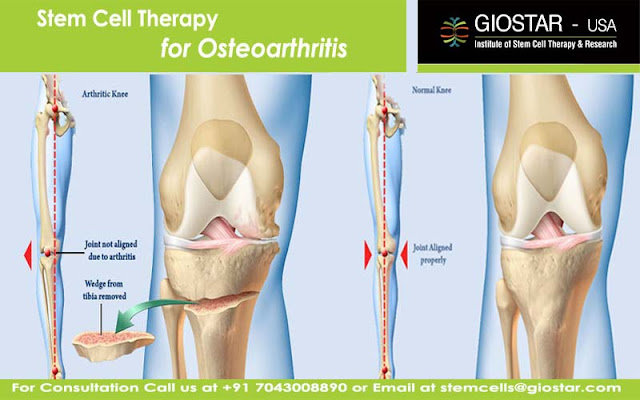
Our joints are
made up of joining of two bones to allow easy movement. These joints are being
protected with the underlying tissue named, cartilages. The cartilages are
soft, spongy tissues; acting as beds in between the two bones. Due to the
presences of these tissues, the friction between the two bones is reduced,
while joints are in mobile state. The cartilages are as well supported with the
presence of synovial fluid, which is helpful in shock absorption. Thus, the
entire assembly can access an easy and long term functionality of joints.
However, variety of issues such as obesity, smoking, poor diet, etc. can create
non significant inflammatory responses, which can degenerate these supportive
tissues such as cartilages and synovial fluid; exposing bones to outer shocks
and friction, leading to their damage.
Stem cells are
the young, privileged cells with the capacity to differentiate into cells of
different origin. The property of stem cells can be uniquely identified to be
potential treatment for arthritis patients. Autologous stem cells isolated from
two different sources such as adipose tissue and/or bone marrow can provide
mesenchymal and hematopoietic stem cells in abundance. These stem cells are
enriched in the laboratory and infused back in the patient’s joints to avail
maximum benefits of tissue function restoration. Once inside the body, these
stem cells are known to reach at the site of injury, due to their strong
communication pathways with other cells, secrete growth factors to reduce the
inflammation and elicit strong immunological reactions to speed up the process
of healing. Stem cells, in case of joints problems or arthritis are known to
induce cells of Chondrocytes origin and get differentiated into cartilages.
Once differentiated into cartilages, there can be reduced friction and pain
associated with OA.
Thus,
considering their anti-inflammatory and regenerative capacities; there are
pretty good reasons to say that these stem
cells can be good candidates for treatment.

Comments
Post a Comment